Vietnam has become an increasingly popular destination for expatriates and foreign workers seeking new opportunities and experiences. However, amidst the excitement of living and working in this vibrant country, it’s crucial for expats to understand their personal income tax obligations. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of personal income tax in Vietnam, shedding light on why expats must fulfill these obligations, the required documents, tax payment locations, common taxes, salary-based tax calculations, tax status, personal income tax rates, and much more. Whether you are a seasoned expat or a newcomer to Vietnam, this guide will help you navigate the complexities of the Vietnamese tax system.
Contents
- 1 Why Expats Must Fulfill Tax Obligations in Vietnam
- 2 Required Documents for Expatriate Tax Payment
- 3 Tax Payment Locations for Expats in Vietnam
- 4 Overview of Common Taxes for Expatriates
- 5 Salary-Based Tax Calculation for Expatriates
- 6 Tax Status and Categories for Foreign Employees
- 7 How to File Personal Income Tax in Vietnam❓
- 8 Social Insurance, Taxable Income, and Employee Benefits
- 9 In-Depth Look at Personal Income Tax Rates
Why Expats Must Fulfill Tax Obligations in Vietnam
👉 Legal Requirement: Expatriates living and working in Vietnam are subject to the same tax laws and regulations as Vietnamese citizens. Failure to comply with these tax obligations can result in legal consequences, including fines and penalties. It’s important to adhere to the law to avoid any potential issues with the authorities.
👉 Avoiding Legal Issues: Non-compliance with tax obligations can lead to legal troubles and could jeopardize an expatriate’s visa or work permit status. Vietnam has stringent immigration and labor laws, and adhering to tax requirements is often a prerequisite for maintaining legal status in the country.
👉 Contributing to Vietnam’s Development: Taxes collected from individuals, including expatriates, play a crucial role in supporting the development of the country. These funds are used to finance public services, infrastructure, and social programs that benefit both citizens and residents. Fulfilling tax obligations is a way of contributing to the growth and well-being of Vietnam as a whole.
👉 Access to Services: Paying taxes ensures that expatriates have access to essential services in Vietnam. This includes healthcare, education, and other public services that are partially funded through tax revenues. By fulfilling tax obligations, expatriates can enjoy the benefits of these services.

👉 Avoiding Future Complications: Failure to pay taxes while residing in Vietnam can lead to difficulties when repatriating or conducting financial transactions in the future. Tax authorities may require proof of tax compliance when dealing with various financial matters, and any outstanding tax issues can complicate these processes.
👉 International Agreements: Vietnam has double taxation agreements with several countries to prevent individuals from being taxed on the same income in both their home country and Vietnam. Fulfilling tax obligations in Vietnam can help expatriates take advantage of these agreements and avoid paying excessive taxes.
👉 Personal Financial Security: Meeting tax obligations allows expatriates to maintain a clean financial record in Vietnam. This is especially important if they plan to invest, purchase property, or engage in other financial activities in the country. A good tax history can enhance financial security and opportunities.
In summary, expatriates in Vietnam must fulfill their tax obligations not only to comply with the law but also to ensure legal standing, contribute to the country’s development, access public services, and safeguard their own financial interests. Understanding and adhering to the tax requirements is a crucial aspect of a successful and trouble-free experience as an expatriate in Vietnam.
Required Documents for Expatriate Tax Payment
To fulfill tax obligations as an expatriate in Vietnam, you will need specific documents and information. Here is a list of the required documents and details necessary for expatriate tax payment:
- Expatriates in Vietnam must obtain a Tax Identification Number (TIN) to conduct any tax-related transactions. You can obtain a TIN from the local tax authority.
- You will typically need to provide a copy of your work permit or employment contract to confirm your employment status and income source in Vietnam.
- Some expatriates may need to provide a residency certificate issued by local authorities or a copy of their temporary residence card to determine their tax residency status.
- Gather all documents related to your income sources, including salary statements, payment receipts, and any other documentation that verifies your earnings in Vietnam.
- Copies of your bank statements can help verify your financial transactions and income sources.
- Complete and submit the necessary tax forms, such as the Personal Income Tax Declaration form, which details your income and tax liability.
- Keep records of all tax payments made, including receipts and transaction records, as proof of your compliance with tax obligations.
- If you are eligible for any tax deductions or exemptions, provide supporting documents, such as receipts for deductible expenses or certificates for tax-exempt income.
- Your passport or other identification documents may be required for identity verification purposes.
- Depending on your specific circumstances and the type of income you earn, you may be asked for additional documents, such as rental agreements (for property income), investment certificates, or business registration documents.
It’s essential to keep these documents organized and up-to-date to facilitate the tax payment process and ensure compliance with Vietnamese tax laws. Additionally, consulting with a tax advisor, such as NN Consulting; or accountant who is familiar with Vietnam’s tax regulations can be beneficial in navigating the documentation requirements and tax obligations effectively.
Tax Payment Locations for Expats in Vietnam
Expatriates in Vietnam can make their tax payments at various locations throughout the country. The specific location and method of payment may depend on the type of tax and your individual circumstances. Here are some common tax payment locations for expatriates in Vietnam:

✅ Local Tax Office: In most cases, you can make tax payments at the local tax office that serves your place of residence or employment. Each province and major city in Vietnam has its own tax office. Visit the local tax office in person to make payments or seek assistance.
✅ Tax Agents and Consultants: Many expatriates in Vietnam choose to work with tax agents or consultants who can assist in preparing and submitting tax payments on their behalf. These professionals are well-versed in the local tax regulations and can ensure compliance.
✅ Online Payment Portals: Some taxes can be paid online through the official website of the General Department of Taxation of Vietnam or through designated online payment portals. You may need to register for an online tax payment account and follow the instructions provided.
✅ Bank Branches: Certain taxes, such as Personal Income Tax in Vietnam, can be paid at authorized bank branches. There are 5 banks in Vietnam where you can pay personal income tax: VietinBank, BIDV, Vietcombank, Agribank, MB Bank.
✅ Online Tax Filing and Payment Platforms: Vietnam has been working to modernize its tax collection system, and there are online tax filing and payment platforms available. These platforms allow you to complete tax-related tasks from the convenience of your home or office.
When making tax payments, ensure that you have all the necessary documentation and information, including your TIN, income details, and any supporting documents required for the specific tax. If you are unsure about the payment process or have questions about tax obligations, consider seeking advice from a tax professional, such as NN Consulting or consulting the local tax office for guidance. Additionally, always keep records of your tax payments and related documents for future reference and proof of compliance.
Overview of Common Taxes for Expatriates
Expatriates living and working in Vietnam may encounter several common taxes. Understanding these taxes is essential for compliance with Vietnamese tax regulations. Here’s an overview of some of the most common taxes that expatriates may encounter:
Income Tax for Foreign Employees
Foreign employees in Vietnam are subject to personal income tax on their earnings. This tax is based on their taxable income, which includes salaries, bonuses, allowances, and other sources of income. The tax rates vary depending on income levels and residency status. Expatriates need to file tax declarations and ensure that their employers withhold the appropriate amount of income tax from their salaries.
Value-Added Tax (VAT)
Value-Added Tax, or VAT, is a consumption tax levied on the value added to goods and services at each stage of production or distribution. While expatriates may not be directly responsible for VAT payments, they should be aware of it, especially if they are involved in business operations in Vietnam. Understanding VAT can be crucial for entrepreneurs and those engaged in business activities.

Social Insurance and Health Insurance
Social insurance and health insurance are mandatory contributions for employees in Vietnam. Expatriates who are legally employed in the country are required to participate in these programs. Social insurance covers various benefits, including sickness, maternity, and retirement. Health insurance provides access to healthcare services. Expatriates and their employers must contribute to these programs based on salary levels.
Property Tax
Property tax applies to individuals who own property in Vietnam. Expatriates who own residential or commercial properties in the country may be subject to property tax. The tax rate and calculation method can vary depending on the type and location of the property. It’s important for expatriate property owners to understand their property tax obligations and comply with the regulations.
Salary-Based Tax Calculation for Expatriates
Salary-based tax calculation for expatriates in Vietnam involves determining the amount of PIT owed based on their earnings, deductions, and applicable tax rates.
First, start by calculating your gross monthly income, which includes your base salary, bonuses, allowances, and any other taxable earnings. This is the total amount you receive before any deductions. Then, determine your taxable income by subtracting any allowable deductions from your gross monthly income. Common deductions may include contributions to social insurance, health insurance, and the mandatory trade union fee. These deductions reduce your taxable income.
Taxable Brackets: In Vietnam, taxable income is divided into different brackets, each subject to its own tax rate. There are seven tax brackets, with corresponding tax rates:
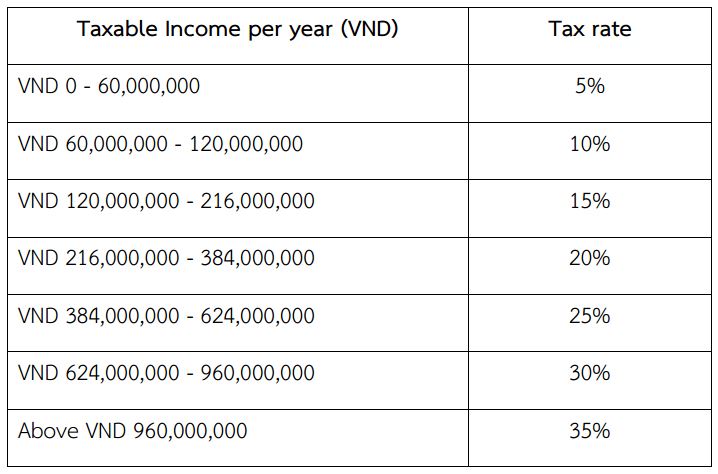
Tax Calculation: Calculate your monthly Personal Income Tax in Vietnam by applying the applicable tax rate to your taxable income within each category. For example, if your taxable income falls within Category 1, you will pay 5% of that income as tax. If it falls within Category 2, you will pay 10%, and so on.
Tax Status and Categories for Foreign Employees
Foreign employees in Vietnam are subject to specific tax statuses and categories that determine their obligations and tax rates. Understanding these classifications is crucial for expatriates to comply with Vietnamese tax regulations.
Tax Residency Status
Foreign employees in Vietnam can have one of the following tax residency statuses:
- Resident Taxpayer: A foreign employee is considered a resident taxpayer if they reside in Vietnam for 183 days or more within a consecutive 12-month period or have a registered permanent residence in Vietnam.
- Non-Resident Taxpayer: A foreign employee is considered a non-resident taxpayer if they do not meet the criteria for resident taxpayer status. Non-resident taxpayers may be subject to different tax rates and obligations.
⭐ Incomes of Foreign Employees in Vietnam
Foreign employees in Vietnam can receive various types of income, each with its own tax implications. Here are some common sources of income for foreign employees:
- Salary and Wages: The primary source of income for foreign employees is their salary or wages earned from their employment. This includes base salary, bonuses, allowances, and other compensation.
- Benefits and Perks: Some foreign employees may receive benefits and perks as part of their employment package, such as housing allowances, transportation allowances, and meal allowances. These may be taxable.
- Business Income: Foreign employees engaged in business activities, such as freelancing or consulting, can earn income from their business operations.
- Rental Income: If a foreign employee owns property in Vietnam and rents it out, the rental income is subject to taxation.
- Investment Income: Income from investments, such as interest, dividends, and capital gains, may also be part of a foreign employee’s income portfolio.
- Other Income Sources: Miscellaneous income sources, such as royalties, awards, and allowances, can contribute to an expatriate’s total income.

⭐ Tax Statements and Settlement Procedures
Foreign employees in Vietnam are required to follow specific procedures for tax statements and settlement. These procedures include:
👉 Monthly Withholding: Employers are typically responsible for withholding and remitting PIT from employees’ salaries on a monthly basis. Personal Income Tax in Vietnam is withheld based on the applicable tax rates and the employee’s taxable income.
👉 Annual Tax Settlement: At the end of each tax year, foreign employees may need to submit an annual tax declaration to reconcile their income and tax liabilities for the year. This process ensures that the correct amount of PIT has been paid.
👉 Payment of Outstanding Taxes: If there are outstanding tax liabilities after the annual settlement, foreign employees are required to pay any remaining taxes to the tax authorities.
👉 Tax Deductions and Exemptions: Foreign employees should be aware of potential tax deductions and exemptions that may apply to their specific circumstances. These can help reduce their overall tax liability.
👉 Record-Keeping: It’s essential for foreign employees to maintain accurate records of their income, deductions, and tax-related documents to facilitate the tax settlement process and provide evidence of compliance with tax regulations.
How to File Personal Income Tax in Vietnam❓

Step 1: Determine Your Tax Residency Status
Step 2: Gather Required Documents and Information
- Collect all relevant financial documents, including salary statements, tax withholding certificates from your employer, and any supporting documents for deductions or exemptions.
- Obtain your Tax Identification Number (TIN) if you don’t already have one.
Step 3: Calculate Your Taxable Income
- Determine your total income for the tax year, including salary, bonuses, allowances, and other earnings.
- Subtract allowable deductions and exemptions to arrive at your taxable income.
Step 4:Complete the PIT Declaration Form
- Obtain a Personal Income Tax Declaration form from the local tax office or download it from the official website of the General Department of Taxation.
- Fill out the declaration form accurately, including your personal information, income details, deductions, and exemptions.
Step 5: Submit the Declaration Form
Submit the completed declaration form and relevant documents to the local tax office that serves your place of residence or employment. You may also be able to submit it online through the tax authority’s website, if available.
Step 6: Pay Any Outstanding Taxes
If you have outstanding taxes after reconciling your income and deductions, you should make the necessary tax payments to the tax authorities.
Step 7: Receive the Tax Assessment Notice
After reviewing your declaration, the tax authorities will issue a tax assessment notice, indicating the final amount of PIT you owe or any tax refund due to you.
Step 8: Payment or Refund
- If you owe additional taxes, make the payment within the specified timeframe.
- If you are eligible for a refund, follow the procedures to receive the refund.
Step 9: Keep Records
Maintain records of all your PIT-related documents, including the declaration form, assessment notices, payment receipts, and any correspondence with tax authorities. These records may be required for future reference or audits.
Step 10: Annual Tax Filing
Repeat the above steps annually, as personal income tax in Vietnam is typically filed on an annual basis.
Step 11: Consult with Tax Professionals
If you have complex tax matter, are unsure about deductions and exemptions, or need assistance with the filing process, consider consulting with tax professionals or advisors who are knowledgeable about Vietnamese tax laws.
Social Insurance, Taxable Income, and Employee Benefits
✅ Social Insurance
Social insurance in Vietnam is mandatory for employees and employers. It covers various benefits, including sickness, maternity, retirement, and more. Contributions to social insurance are typically withheld from employees’ salaries and matched by employers. Social insurance contributions are considered deductible expenses for PIT purposes.
✅ Taxable Income
Taxable income includes all earnings, such as salaries, bonuses, allowances, and other forms of compensation. To calculate taxable income, deductions and exemptions, including social insurance contributions, are subtracted from gross income.
✅ Employee Benefits
Employee benefits can include housing allowances, transportation allowances, meal allowances, and other perks provided by employers. These benefits may be taxable or exempt from PIT, depending on specific criteria and regulations.
Taxable Income in Foreign Currency

- Income received in foreign currency is generally subject to taxation in Vietnam.
- The exchange rate used to convert foreign currency into Vietnamese Dong (VND) for tax purposes is typically the exchange rate published by the State Bank of Vietnam on the date of the transaction.
- Foreign currency income should be reported in VND when calculating taxable income for PIT purposes.
- Expatriates should maintain records of foreign currency transactions and conversion rates for tax documentation.
Tax Reduction and Exempt Incomes
Tax Reduction
- Tax reduction can be granted to individuals with disabilities or individuals who are the sole breadwinners of households facing difficult circumstances. These reductions are subject to specific criteria and application processes.
- Expenses related to scientific research and technological development can also be eligible for tax deductions.
Exempt Incomes
- Certain types of income may be exempt from PIT, such as income from life insurance policies, gifts, and inheritances.
- Expatriates should be aware of potential exemptions applicable to their specific circumstances and income sources.
- Income exempt from Personal income tax in Vietnam may still be subject to other taxes or regulations, so it’s important to understand the complete tax treatment.
In-Depth Look at Personal Income Tax Rates
✅ Tax Rates for Different Incomes and Residency Status
Tax rates in Vietnam can vary not only based on income levels but also on residency status. Here’s an overview of how tax rates may differ for different groups:
Resident Taxpayers
- Resident taxpayers are individuals who meet the criteria for tax residency in Vietnam.
- They are subject to the progressive tax rates mentioned earlier.
Non-Resident Taxpayers
- Non-resident taxpayers, including some expatriates, may be subject to different tax rates for certain types of income.
- For example, non-resident taxpayers may face a flat tax rate on income earned in Vietnam, such as business income or rental income, which could be higher than the rates applied to resident taxpayers.
- The tax treatment of non-resident taxpayers can vary based on specific tax treaties between Vietnam and other countries.
✅ NN Consulting Services for Personal Income Tax in Vietnam
| ⭐⭐ PIT Services For Foreigners in Vietnam | Bookkeeping Service, Payroll Service, VAT Filing Service, Tax Declaration Service, PIT Return for Foreigners, Expat, Resident and Non-Resident Service |
| ⭐⭐ Hotline | +84 924453930 |
| ⭐⭐ Benefits | Professionalism and Experience, Time Saving, Cost Optimization |
| ⭐⭐ Advantages | Service: Efficient, Fast, Optimized |
| ⭐⭐ Commitment | Compliance with the Law, Professional Process, Help Business Save Time and Expense |
NN Consulting provides a range of services to assist individuals, including expatriates, with their personal income tax in Vietnam.
⭐ Tax Compliance: We can help individuals ensure that they are complying with Vietnamese tax regulations by providing guidance on tax payments, deductions, and exemptions.
⭐ Tax Planning: The company may offer tax planning services to optimize an individual’s tax situation, taking advantage of deductions and exemptions while legally minimizing tax liabilities.
⭐ Tax Documentation: NNC can assist with the preparation of necessary tax documentation, including annual tax returns and supporting financial records.
⭐ Consultations: Individuals can consult with NNC experts to address specific questions or concerns related to personal income tax in Vietnam.
⭐ Updates and Compliance: NNC stays updated with changes in tax laws and regulations, helping clients remain compliant with the latest requirements.




