Navigating the complexities of personal income tax in a foreign country can be a daunting task for expatriates and foreign workers. In Vietnam, understanding the nuances of personal income tax in Vietnam 2024 is not only a legal obligation but also a critical component of sound financial planning and compliance.
For expatriates living and working in Vietnam, staying informed about PIT is essential. The tax system in Vietnam may differ significantly from that of their home countries, encompassing unique rules, rates, and regulations. Let’s dive into this article to learn more about PIT for Expats in Vietnam 2024.
Contents
- 1 Cases Eligible for Personal Income Tax Finalization
- 2 Document Submission for Personal Income Tax Finalization
- 3 Special Considerations for Foreign Workers
- 4 Overview of Personal Income Tax Rates 2024
- 5 Foundational Principles for Personal Income Tax Finalization
- 6 Engaging Assistance at NN Consulting for Personal Income Tax in Vietnam 2024
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about Personal Income Tax in Vietnam 2024
Cases Eligible for Personal Income Tax Finalization
Understanding which cases are eligible for personal income tax in Vietnam 2024 is crucial for expatriates and foreign workers. Personal income tax finalization is a process where individuals settle their tax obligations, ensuring that the actual tax paid aligns with the legal requirements for the fiscal year. Here are the key scenarios where expatriates are required or eligible to finalize their personal income tax in Vietnam 2024:
Direct Finalization with Tax Authorities
- Expatriates Without a Tax Withholding Agent: Individuals who do not have employers acting as tax withholding agents in Vietnam need to directly finalize their taxes with the local tax authorities. This circumstances often applies to freelancers, consultants, or those engaged in independent contract work.
- Leaving Vietnam Before Tax Year Ends: Expatriates planning to leave Vietnam before the end of the tax year are required to finalize their taxes directly with the tax authorities before their departure.
- Income from Various Sources: For those receiving income from multiple sources, such as different employers or a combination of employment and business income, direct finalization is necessary to accurately report and settle their total tax liability.

Personal Income Tax Finalization Dossiers and Procedures
1. Required Documents:
- Tax finalization declaration form.
- Valid identification documents (passport, resident card).
- Documents substantiating income and tax withheld (if applicable), such as income statements, tax withholding certificates from employers.
- Other relevant documents based on specific income types or deductions claimed.
2. Procedures:
- Submit the tax finalization dossier to the local tax department where the taxpayer is registered.
- The submission can be done physically at the tax office or electronically through official online tax services, if available.
- The deadline for tax finalization is typically the 90th day from the end of the calendar year, but it’s advisable to check for any specific deadlines for the current year.
3. Tax Calculation and Payment:
- Taxpayers need to calculate their taxable income, apply the relevant tax rates, and determine the tax amount due or the refundable amount if they have overpaid.
- Any tax owed must be paid by the finalization deadline. Overpaid taxes may be refunded or carried forward to the next tax period.
4. Receipt of Finalization Confirmation:
Upon the successful processing of your tax finalization dossier by the Vietnamese tax authorities, you will receive a finalization confirmation. This document serves as a crucial piece of evidence, affirming that you have met all your tax obligations for the given fiscal year in Vietnam.
It is important for expatriates to be aware of these requirements and procedures to ensure proper compliance and avoid any potential penalties or legal issues. Consulting with a tax professional or utilizing the services of a tax consultancy firm, like NN Consulting, can be highly beneficial in navigating these processes.
Document Submission for Personal Income Tax Finalization
For expatriates in Vietnam, the process of personal income tax finalization involves meticulous document submission to ensure compliance and accurate tax calculation. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Specific Deadline Guidelines for 2024 Finalization
- Submission Deadline: The deadline for submitting personal income tax finalization documents for the year 2024 is typically the 90th day from the end of the calendar year. Which falls around the end of March 2024. It’s crucial to adhere to this deadline to avoid penalties.
- Documents Required: The submission should include a tax finalization declaration form, proof of income, tax payment receipts, and any applicable documents for tax deductions or exemptions. Expatriates should also provide valid identification and residency documentation.
- Electronic Submission: Where available, taxpayers can opt for electronic submission through the official tax portal, which is a convenient and efficient method.
- Physical Submission: If electronic submission is not an option, taxpayers should submit their documents to the local tax office where they are registered.

Highlights of the Personal Income Tax Finalization Deadline in 2024
- Anticipated Deadline: For 2024, thePIT finalization deadline is expected to remain similar, around the end of March 2025. However, it’s advisable to stay informed about any changes or specific dates announced by the Vietnamese tax authorities.
- Planning Ahead: Taxpayers should begin preparing their documents well in advance of the deadline. Early preparation allows for addressing any discrepancies in income or tax payments and seeking professional advice if needed.
- Changes and Updates: Be attentive to any changes in tax laws or procedures that may affect the finalization process for 2024. Vietnamese government may implement new regulations or amendments that could impact tax calculations or submission methods.
- Professional Assistance: Considering potential changes and the complexity of tax laws, engaging with tax professionals or consultancy services for the 2024 tax year can be beneficial. Especially for expatriates unfamiliar with the Vietnamese tax system.
Special Considerations for Foreign Workers
Foreign workers in Vietnam may face different tax issues that differ from local taxpayers. Understanding these distinctions is critical for accurate tax planning and compliance. Special considerations mainly revolve around residency status, types of income, and applicable tax treaties.
Global Income Insights for Expatriates
1. Residency Status and Global Income:
– The tax liability of an expatriate in Vietnam largely depends on their residency status. A resident is typically taxed on their worldwide income, whereas a non-resident is taxed only on Vietnam-sourced income.
– Residency is generally determined based on the number of days an individual spends in Vietnam in a calendar year. The specific criteria can be found in Vietnamese tax legislation.
2. Taxation of Global Income:
– For expatriates classified as residents, it’s important to understand how global income is taxed. This includes income earned both within and outside Vietnam.
– Expatriates should declare all sources of income, including wages, interest, dividends, rental income, and any other income, regardless of where it is earned.
3. Double Taxation Agreements (DTAs):
– Vietnam has DTAs with many countries to prevent double taxation of income earned in one country by a resident of another. These agreements can significantly impact how expatriates are taxed.
– Expatriates should determine if a DTA exists between Vietnam and their home country and understand how it affects their tax liabilities.
4. Foreign Tax Credits:
Under certain conditions, expatriates may be eligible for foreign tax credits for taxes paid in other countries. This can reduce the overall tax burden in Vietnam.
5. Documentation and Reporting:
– Proper documentation and reporting of global income are vital. Expatriates should keep detailed records of their income and taxes paid in other jurisdictions.
– It’s advisable to seek professional advice to ensure all international income is accurately reported and taxed in compliance with Vietnamese laws and any applicable DTAs.
6. Planning and Compliance:
– Understanding the nuances of global income taxation is crucial for effective tax planning and compliance. This includes being aware of any changes in tax laws that might affect expatriates.
– Engaging in early tax planning and consulting with tax professionals can help expatriates navigate the complexities of global income taxation in Vietnam.

In summary, for expatriates working in Vietnam, a thorough understanding of how global income is taxed and the implications of residency status are essential. Awareness of and compliance with the relevant tax laws and international agreements can help in effective tax planning and avoiding legal complications.
Overview of Personal Income Tax Rates 2024
Tax Rates and Calculations for Non-Resident Individuals
1. Flat Tax Rate: Non-resident individuals in Vietnam are typically subject to a flat tax rate. As of my last update in April 2024, this rate was 20%, but it’s important to verify the current rate as tax laws may have changed.
2. Taxable Income: For non-residents, only income earned from sources within Vietnam is taxable. This includes wages, rental income, and other earnings originating from Vietnamese entities or activities.
3. No Progressive Tax Slabs: Unlike residents, non-resident individuals do not benefit from progressive tax rates. They are taxed at the same flat rate regardless of their income level.
4. Calculations: To calculate the tax, simply apply the flat tax rate to the total Vietnam-sourced income. For example, if a non-resident earns 100,000,000 VND in Vietnam, their tax would be 20% of that amount.
Tax Rates and Bases for Resident Individuals
1. Progressive Tax Rates: Resident individuals are subject to progressive tax rates. These rates increase with the level of income, making it important to understand which tax bracket applies to your income level.
2. Taxable Income: For residents, global income (income from both Vietnamese and foreign sources) is subject to tax. However, exemptions and deductions can apply, reducing the taxable base.
3. Tax Brackets: The progressive tax rates are divided into several brackets. Each bracket corresponds to a specific range of income and has an associated tax rate. As your income increases, a higher rate applies to the portion of income within that higher bracket.
4. Calculations and Deductions: To calculate the tax, apply the respective tax rate to each portion of your income within each bracket. Residents can also take advantage of personal deductions, family allowances, and other tax reliefs, which can significantly reduce the taxable income.
5. Staying Informed: Tax rates and regulations can change, so it’s important for expatriates to stay updated. Professional advice or consulting a tax expert is advisable for accurate tax calculations and planning.
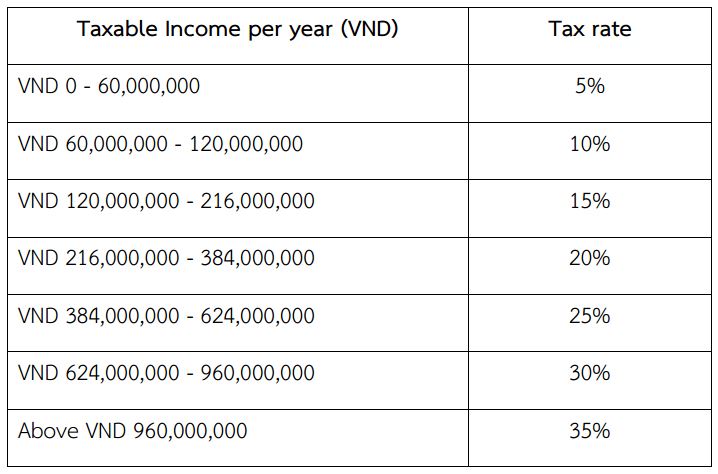
Understanding these tax rates and their application is key for expatriates and foreign workers in Vietnam to ensure compliance and effective financial planning. The distinction between resident and non-resident tax treatments highlights the importance of determining your residency status for tax purposes.
Foundational Principles for Personal Income Tax Finalization
When dealing with personal income tax finalization in Vietnam 2024, it’s important for expatriates and foreign workers to understand the foundational principles that underpin the process. These principles form the basis of the Vietnamese tax system and guide taxpayers in their compliance and finalization efforts. Here are the key principles to consider:
- Taxpayer Responsibility: The primary responsibility for declaring and finalizing personal income tax rests with the individual taxpayer. This includes accurate reporting of income, claiming applicable deductions, and ensuring timely submission of tax documents.
- Progressive Taxation for Residents: Vietnam employs a progressive tax system for residents, where the tax rate increases as the taxable income increases. This principle reflects the ability-to-pay concept, ensuring that those with higher incomes contribute more in taxes proportionally.
- Flat Tax Rate for Non-Residents: Non-resident individuals are subject to a flat tax rate on their Vietnam-sourced income. This simplifies the tax calculation for those not residing in Vietnam for extended periods.
- Global Income Taxation for Residents: Residents are taxed on their worldwide income, not just the income earned within Vietnam. This principle emphasizes the global scope of tax liability for residents. Which makes it essential to declare all sources of income.
- Source Principle for Non-Residents: Non-residents are taxed only on income sourced from Vietnam. The source principle ensures that Vietnam taxes income earned within its jurisdiction for those not classified as residents.
- Tax Deductions and Credits: The Vietnamese tax framework permits various deductions and credits to decrease taxable income, including personal and dependents’ allowances and specific expense deductions, supporting equitable taxation.
- Legal Compliance and Penalties: Adhering to tax laws and deadlines is fundamental. Non-compliance, late filing, or incorrect declarations can lead to penalties, emphasizing the importance of accuracy and timeliness in tax matters.
- Confidentiality and Privacy: Taxpayer information is treated with confidentiality. The tax authorities are responsible for ensuring that personal and financial information is securely handled and protected.
- Double Taxation Avoidance: With multiple bilateral agreements to prevent double taxation, Vietnam ensures that expatriates don’t face dual tax liabilities in different countries.
- Annual Finalization: PIT in Vietnam is finalized annually. This practice allows taxpayers to reconcile their tax payments and ensures that they have paid the correct amount of tax for the year.

Engaging Assistance at NN Consulting for Personal Income Tax in Vietnam 2024
For expatriates and foreign workers in Vietnam, managing personal income tax in Vietnam 2024 can be complex and challenging. Engaging with NN Consulting provides specialized assistance to navigate this process smoothly. Below is an overview of our services and what makes us stand out in the field of tax consultancy.
Our Services
⭐ Comprehensive Tax Consultation: We offer detailed consultations to understand your unique tax situation, considering factors like residency status, income sources, and applicable tax treaties.
⭐ Tax Filing, Declaration, Finalization: Our tailored approach ensures accurate compliance with local tax laws, while efficiently managing the complexities of tax obligations for expatriates and foreign workers.
We guide our clients through each step of the process, from initial assessment to the finalization of tax returns, ensuring a smooth and stress-free experience. Our commitment lies in delivering personalized service, ensuring that all tax-related matters are handled with utmost professionalism and attention to detail.
⭐ Tax Refund Preparation and Filing: Our team assists in preparing and filing your tax returns accurately. Which ensures compliance with the latest Vietnamese tax laws and regulations.
⭐ Representation in Tax Matters: We represent our customers in dealings with the Vietnamese tax authorities, providing support during audits, inquiries, and negotiations.
⭐ Tax Planning and Advisory: Our experts provide strategic tax planning advice. Which helps foreigners to optimize your tax position and take advantage of applicable deductions and credits.

What Sets Us Apart?
| ⭐⭐ PIT Services For Foreigners in Vietnam | Bookkeeping Service, Payroll Service, VAT Filing Service, Tax Declaration Service, PIT Return for Foreigners, Expat, Resident and Non-Resident Service |
| ⭐⭐ Hotline | +84 924453930 |
| ⭐⭐ Benefits | Professionalism and Experience, Time Saving, Cost Optimization |
| ⭐⭐ Advantages | Service: Efficient, Fast, Optimized |
| ⭐⭐ Commitment | Compliance with the Law, Professional Process, Help Business Save Time and Expense |
✅ Expertise and Experience: Our team consists of experienced tax professionals with deep knowledge of Vietnamese and international tax laws. This expertise ensures high-quality service and reliable advice.
✅ Customized Solutions: We understand that each client’s situation is unique. Our approach is to provide personalized solutions tailored to meet the specific needs of each individual.
✅ Language and Cultural Understanding: Being proficient in multiple languages and having a deep understanding of both local and expatriate cultures, we bridge communication gaps and provide a comfortable consulting experience.
Frequently Asked Questions about Personal Income Tax in Vietnam 2024
As the 2024 tax year progresses, numerous questions arise regarding personal income tax in Vietnam, especially for expatriates and foreign workers. Addressing these FAQs can provide clarity and help in navigating the tax landscape.
Recent Updates and Insights in Taxation
1. What documentation is required for tax declaration in 2024?
For individuals directly finalizing PIT with the tax authorities, the 2024 PIT finalization dossier includes:
- Personal income tax finalization declaration form (Model 02/QTT-TNCN).
- Appendix for the dependent family member deduction schedule (Model 02-1/BK-QTT-TNCN).
- Copies (from the original) of documents proving the amount of tax withheld, temporarily paid during the year, and tax paid abroad (if applicable).
For organizations and individuals paying income, the 2024 PIT finalization dossier includes:
- Personal income tax finalization declaration form (Model 05/QTT-TNCN).
- Appendix detailing individuals subject to tax on a progressive scale (Model 05-1/BK-QTT-TNCN).
- Appendix detailing individuals subject to tax at full rates (Model 05-2/BK-QTT-TNCN).
- Appendix for the detailed schedule of dependent family member deductions (Model 05-3/BK-QTT-TNCN).
2. How to Calculate Personal Income Tax for Foreigners in Vietnam?
For foreigners classified as resident individuals:
- A resident individual is someone who stays in Vietnam for 183 days or more in a calendar year or over 12 consecutive months. Or, they have a permanent residence in Vietnam as per residency regulations or a rental agreement in Vietnam for 183 days or more.
- The tax for resident individuals is applied on a progressive scale, meaning the higher the income, the higher the tax rate.
For foreigners who are not resident individuals:
- Non-resident individuals are those who do not meet the conditions of resident individuals.
- Tax calculation: Personal Income Tax = Taxable Income x 20%.
3. How do the changes in tax laws affect expatriates?
Changes in tax laws can significantly impact expatriates in Vietnam, potentially altering their tax liabilities and filing requirements. Adjustments in tax rates, brackets, or available deductions directly affect the amount of tax owed.
For those classified as residents, alterations in the treatment of global income can have substantial implications on their overall tax burden. Furthermore, modifications in documentation or filing procedures necessitate staying updated to ensure compliance. It’s crucial for expatriates to remain informed about these changes and, if necessary, seek professional advice to navigate the new tax landscape effectively.
Conclusion
Navigating the personal income tax landscape in Vietnam, particularly in 2024, requires staying informed and proactive. With the ever-evolving tax regulations and their implications, especially for expatriates and foreign workers, understanding the nuances is crucial. Whether it’s adapting to new tax rates, leveraging available deductions, or complying with documentation requirements, a thorough grasp of these aspects is key to effective tax management.
At NN Consulting, we committed to provide our clients with the most current insights and tailored assistance. Which ensures a seamless and compliant tax experience in Vietnam. Remember, staying ahead of the changes and seeking professional advice can make a significant difference in your personal income tax journey.




